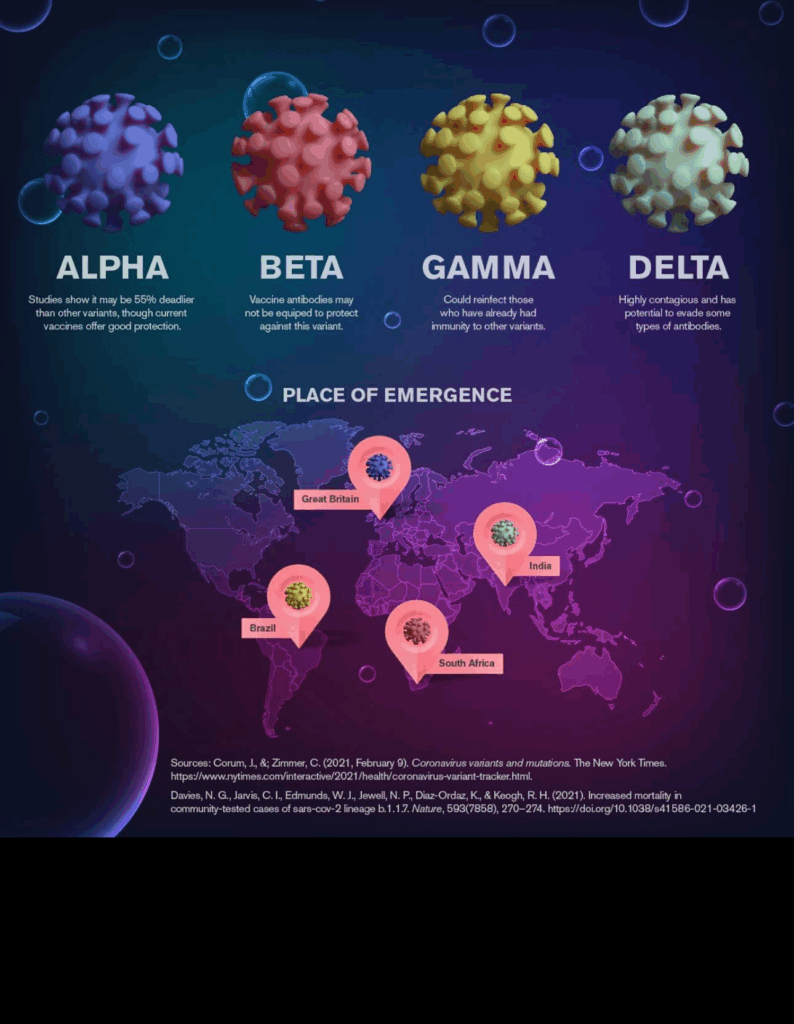
A new COVID-19 variant, NB.1.8.1, is making its way across the U.S., with confirmed cases in states like California, Ohio, and Hawaii . This subvariant, a descendant of Omicron, is noted for its high transmissibility, though current data suggests it doesn’t cause more severe illness than previous strains . Despite the emergence of NB.1.8.1, the federal government has announced plans to limit access to COVID-19 vaccines. Under new guidelines, routine vaccinations are no longer recommended for healthy children and pregnant women. Instead, boosters will primarily be available to seniors and individuals with high-risk health conditions . Health experts express concern that these policy changes could lead to reduced vaccination rates and increased vulnerability, especially among populations previously encouraged to receive the vaccine. As the situation evolves, staying informed and adhering to public health recommendations remains crucial.




